Aaron Naeger
@naegeraaron
Research scientist @NASA_Marshall @NASA_SPoRT. Mission Applications Lead @TEMPO_Mission. Air quality+weather+satellite+travel+fitness enthusiast. Tweets my own.
ID: 1302355751600496642
05-09-2020 21:19:49
1,1K Tweet
507 Followers
328 Following

AGU_GeoHealth NASA’s MAIA mission will use satellite data to study how air pollution affects human health! Use this interactive tool to learn about MAIA target areas, explore their geospatial characteristics, and access ground PM2.5 and PM10 data from these regions maia.jpl.nasa.gov/mmgis/


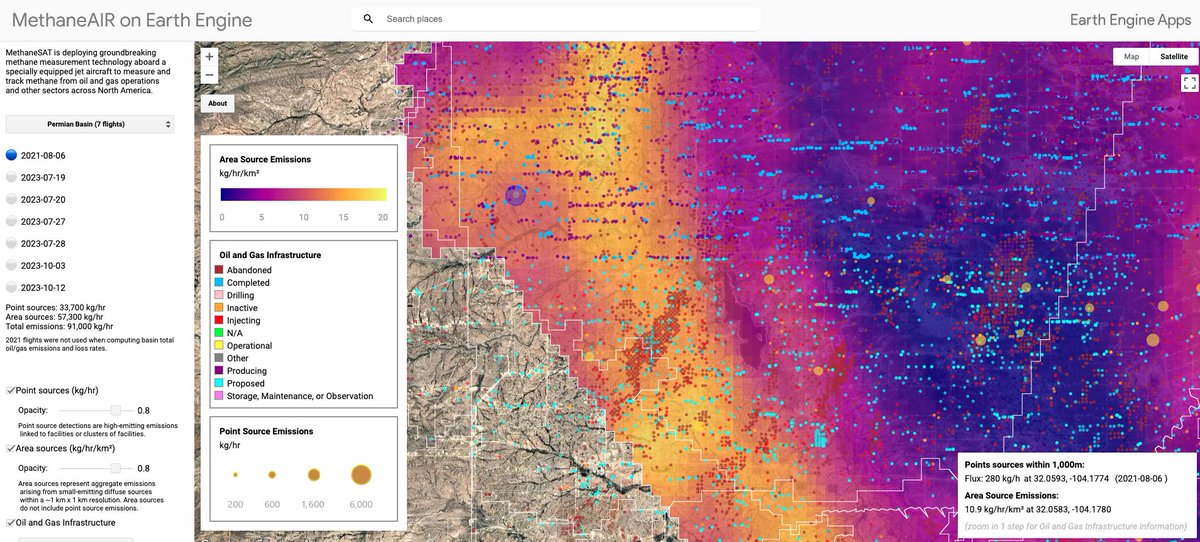
Data update: We have added oil and gas infrastructure data to our methane map on Google Earth engine🗺️ You can filter the O&G facilities by category and status, while overlaying it with emissions data from our MethaneAIR campaign 🔎 Check it out here: showcase.earthengine.app/view/methanesat

Groundbreaking TEMPO Mission highlights urban nitrogen dioxide (NO2) emissions (red/orange/yellow/teal shading) across the CONUS, southern Canada & northern Mexico yesterday afternoon 3 Oct. Dan Goldberg, PhD Aaron Naeger NASA HAQAST Joel Dreessen Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian NASAEarthdata

Revolutionary #TEMPO geostationary sensor observed accumulation of urban nitrogen dioxide (NO2) emissions across the CONUS yesterday afternoon 24 Oct, especially from #NewYorkCity, #Chicago, #Houston & #LosAngeles. TEMPO Mission Dan Goldberg, PhD Aaron Naeger

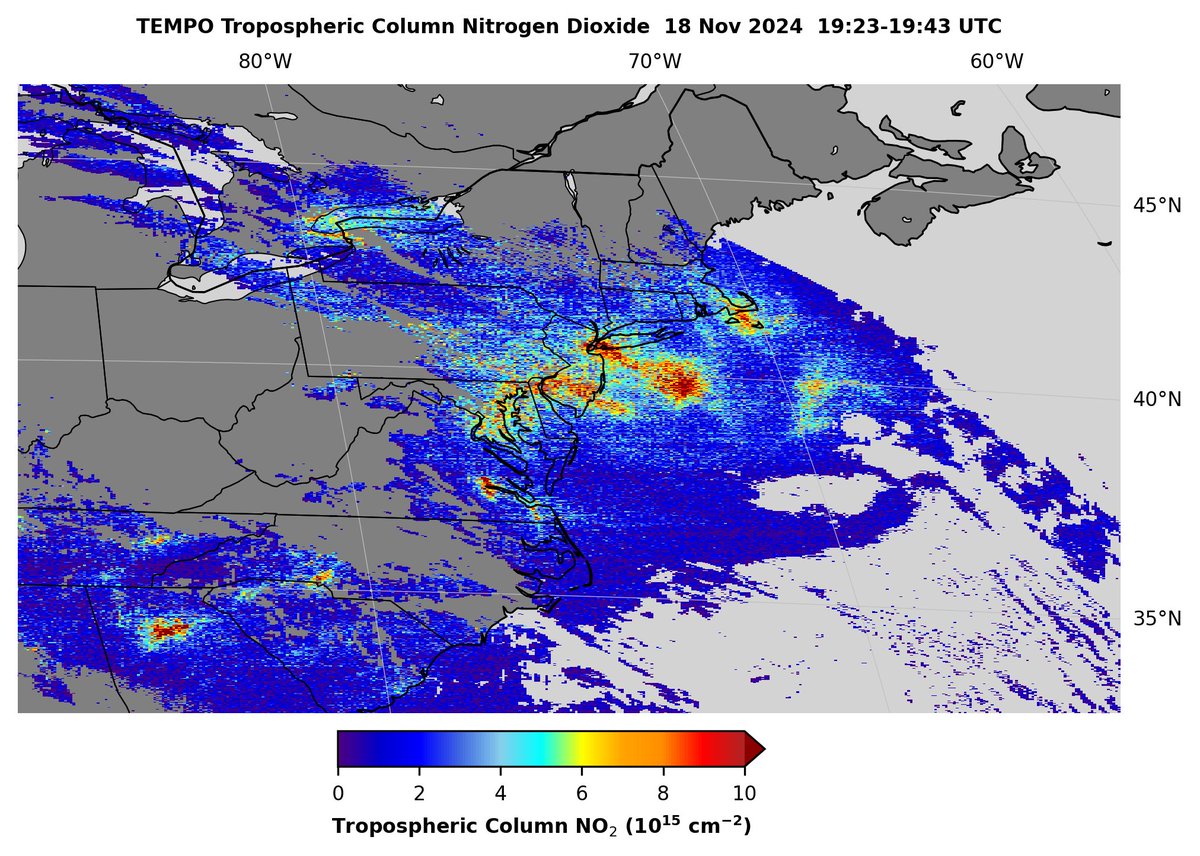
#TEMPO geostationary satellite sensor observed buildup of nitrogen dioxide (NO2) emissions in the eastern US on 18 Nov, particularly from the Northeast urban corridor, Richmond Virginia, Charlotte North Carolina, and Atlanta Georgia. TEMPO Mission Aaron Naeger Dan Goldberg, PhD

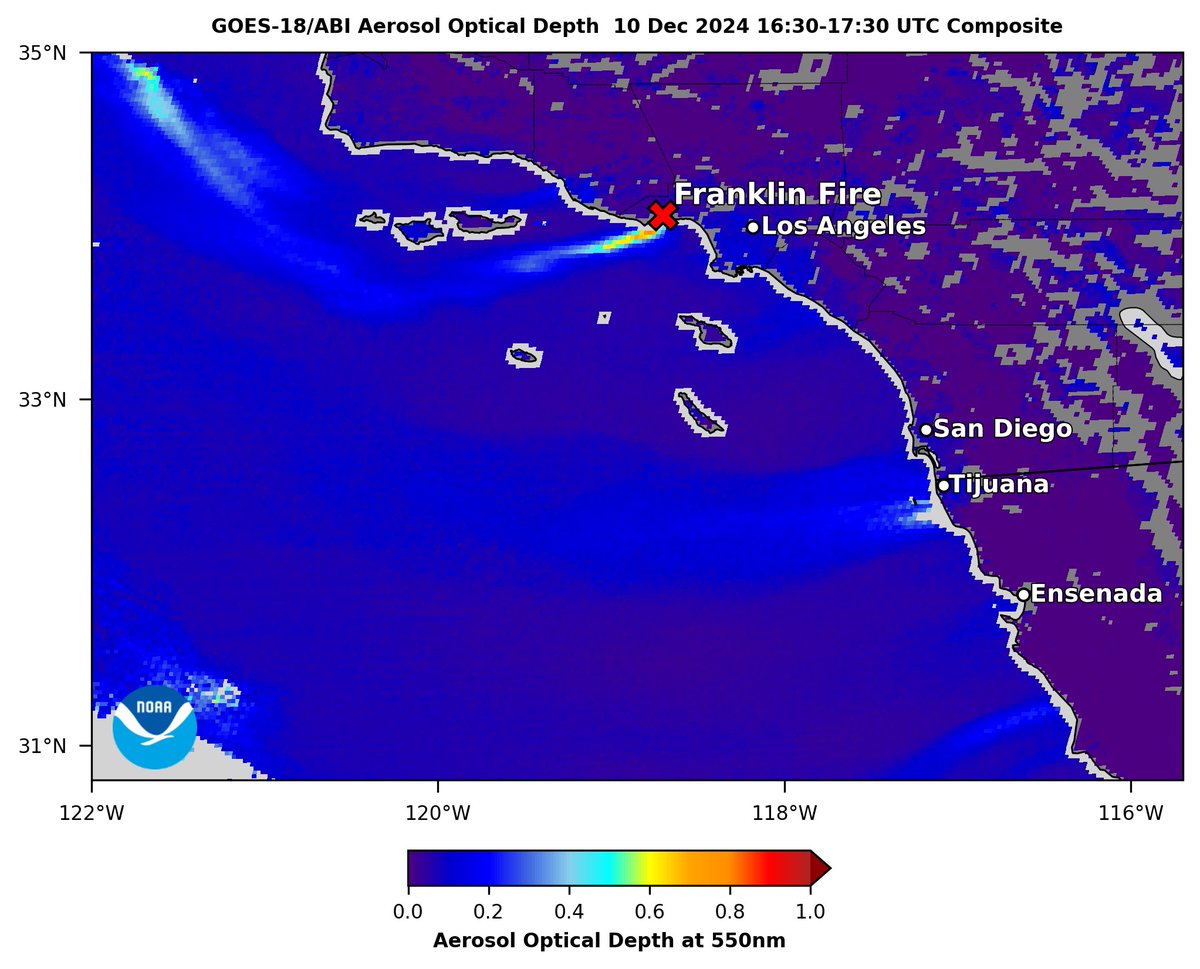
#GOESWest #ABI aerosol optical depth (AOD) shows #smoke from fast-growing #FranklinFire in #Malibu this morning 10 Dec, driven by #SantaAna winds, which are also blowing #dust off the coast of #BajaCalifornia near #Tijuana & south of #Ensenada. CAL FIRE Tim Schmit NOAA Satellites

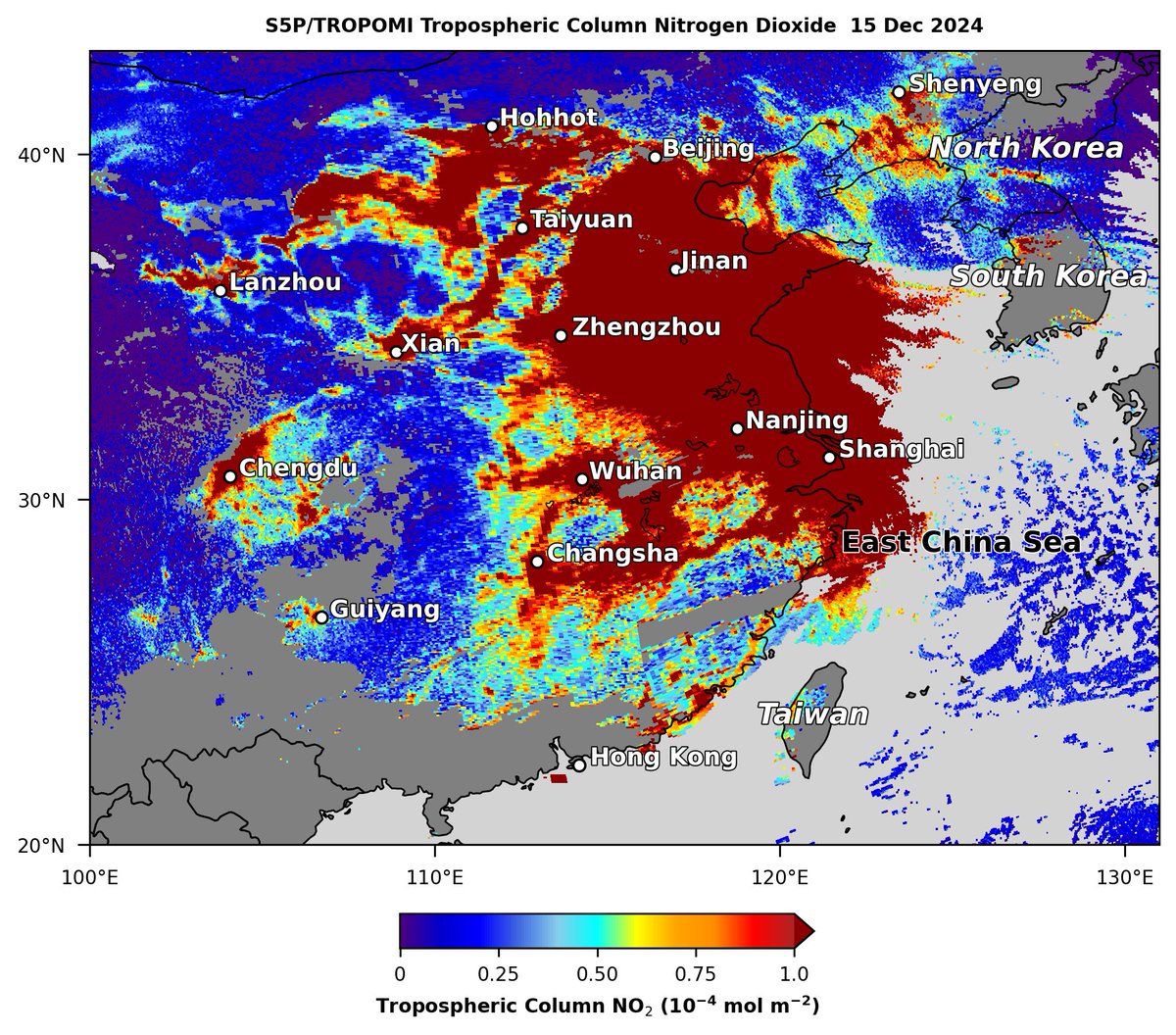
#Sentinel5P #TROPOMI observed very high nitrogen dioxide (NO2) emissions (dark red shading), likely from urban & industrial sources, covering eastern #China on 15 Dec, including cities of #Beijing, #Shanghai, #Zhengzhou & #Nanjing. Copernicus EMS Dan Goldberg, PhD Aaron Naeger

Check out this visualization from NASA's Scientific Visualization Studio that shows how the Atmospheric Composition instrument (ACX) on the NOAA Satellites next-gen Geostationary Extended Observations (GeoXO) satellites will monitor pollution hourly over the US during the daytime! svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/5132

New TEMPO Mission aerosol products include a NOAA Satellites ABI hybrid Aerosol Detection Product (ADP), featuring the UV Absorbing Aerosol Index (AAI) that highlights smoke & dust aerosols in the atmosphere. Phurbu Aaron Naeger

New TEMPO aerosol products include hourly surface PM2.5 concentrations estimated from TEMPO Mission & NOAA Satellites ABI aerosol retrievals, which fill gaps in observations from airnow regulatory monitor networks. Aaron Naeger Joel Dreessen Cary Gentry

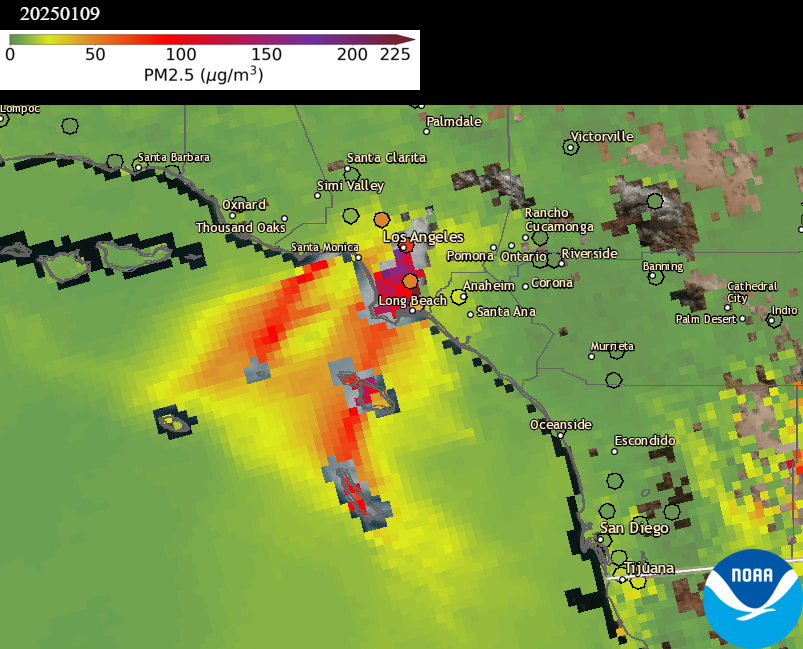
The Southern California wildfires, particularly the Palisades & Eaton Fires, continued to emit very thick smoke on 9 Jan (Left, VIIRS aerosol detection product, ADP), driven by Santa Ana winds, causing poor daily PM2.5 air quality (Right) in the LA metro area. NOAA Satellites

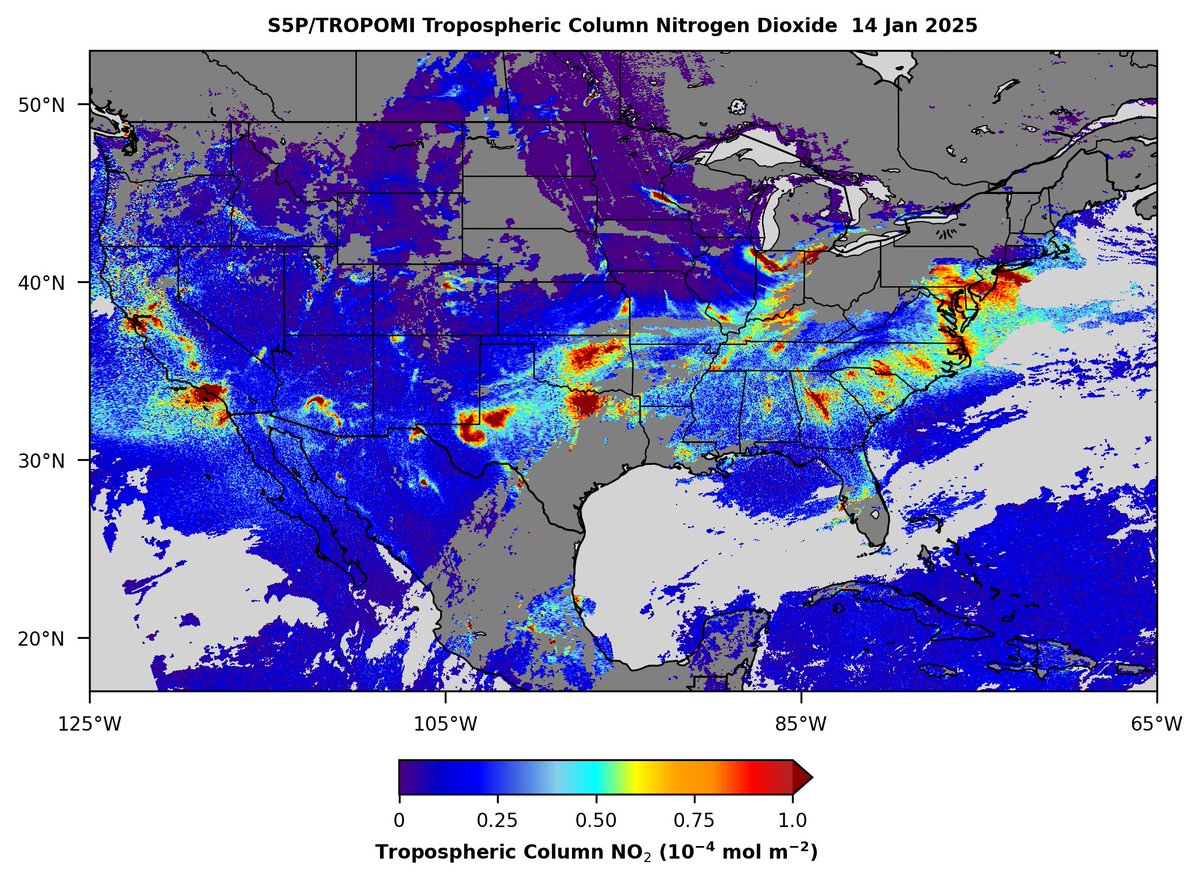
Sentinel-5P TROPOMI observed build-up of tropospheric nitrogen dioxide (NO2) across North America yesterday 14 Jan, particularly emissions from urban areas of the continental US. Gaps in NO2 measurements are due to cloud cover. Copernicus EMS Dan Goldberg, PhD Aaron Naeger

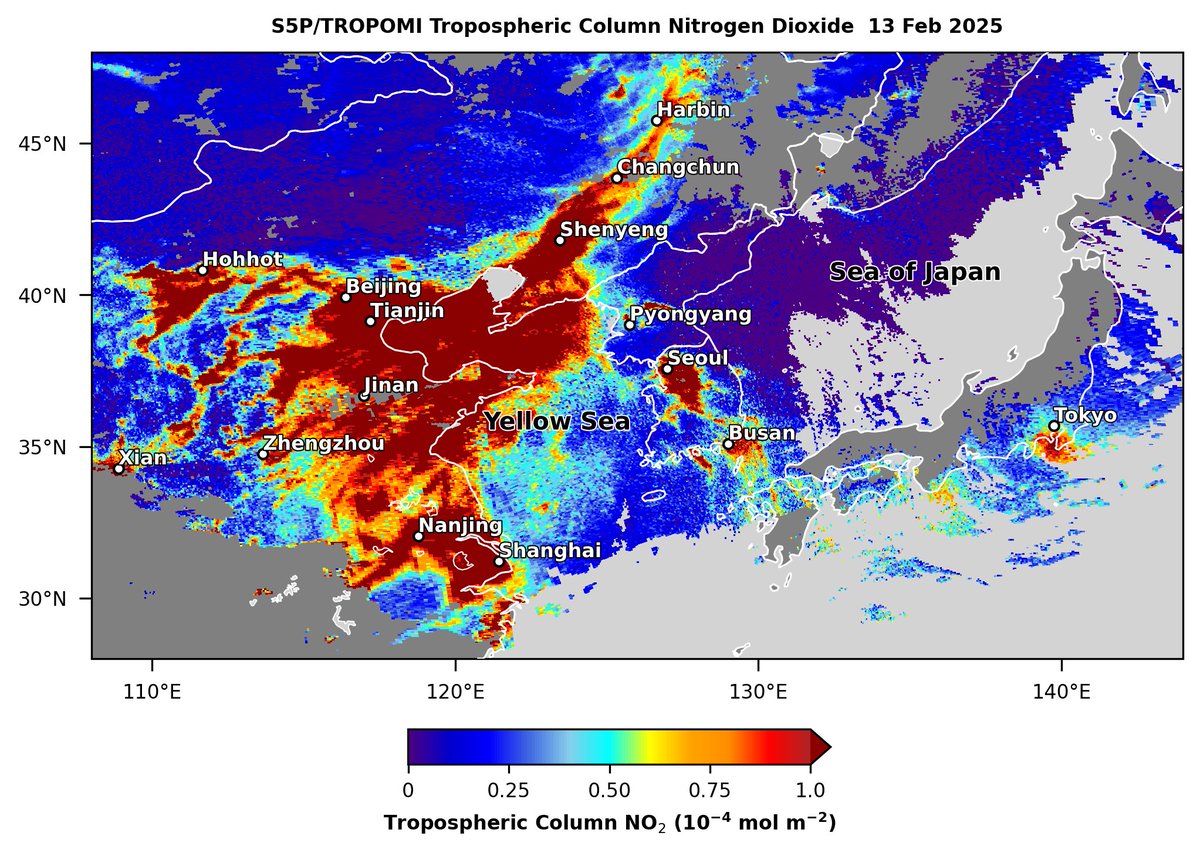
Under mostly clear skies across eastern Asia on Feb 13, Sentinel5-P TROPOMI observed high nitrogen dioxide (NO2) emissions (dark red shading) from urbanized regions of China, South Korea, North Korea & Japan. Copernicus EMS Aaron Naeger

High plumes of nitrogen dioxide (NO2) (dark red shading) in Alberta Canada, associated with oil & gas activities and urban emissions, were observed on 18 Feb by the TROPOMI sensor on the Sentinel5-P satellite. Copernicus EMS Aaron Naeger


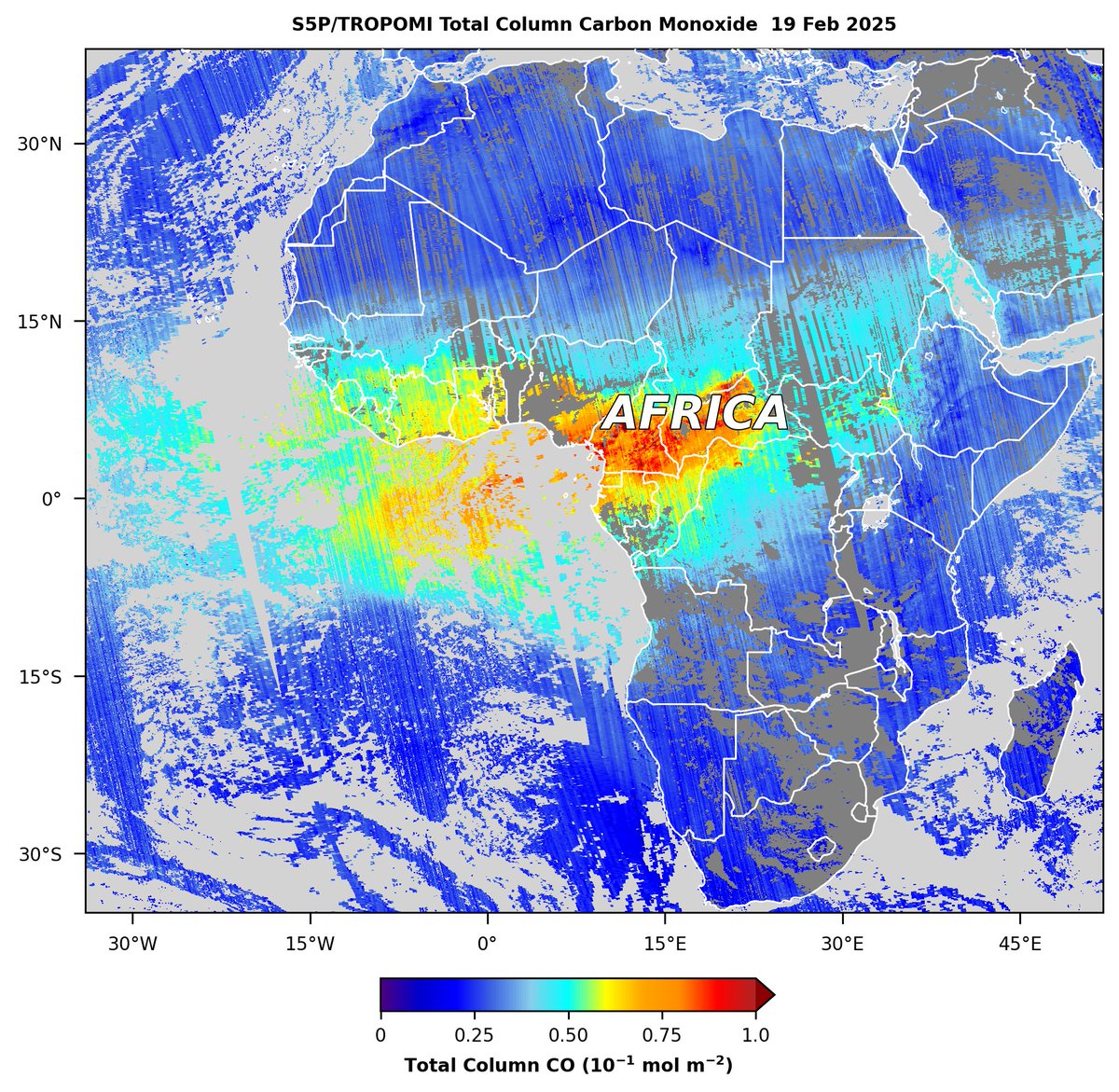
Seasonal burning in central Africa is emitting large amounts of carbon monoxide (CO), as observed on 19 Feb by the TROPOMI sensor on the Sentinel 5-P satellite. Copernicus EMS Aaron Naeger ESA Earth Observation

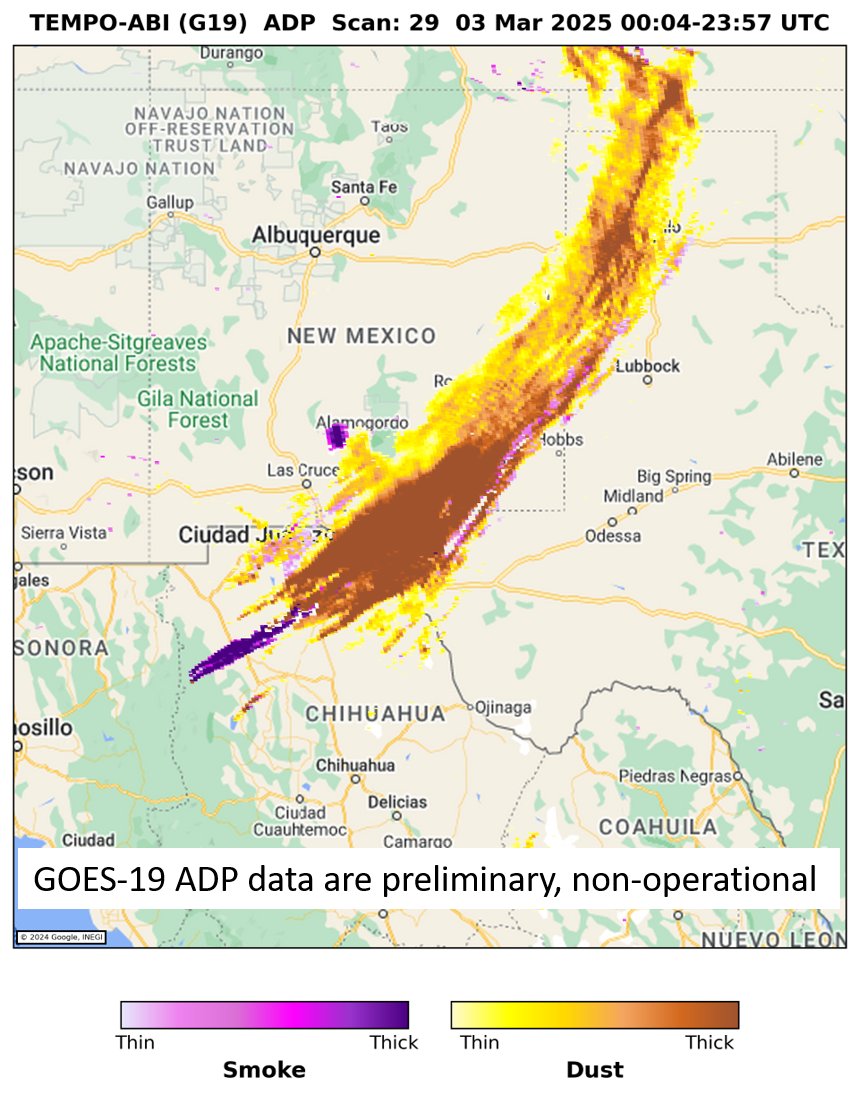
New Aerosol Detection Product (ADP) from merged TEMPO & GOES-19 ABI observations highlights blowing dust along a cold front across TX & NM on 3 Mar; yellow indicates thin dust & dark brown indicates thick dust. Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian TEMPO Mission NOAA Satellites Phurbu